Insight Focus
President Trump has already sparked debates over US control of the canal. His push for reclamation signals a more aggressive stance with global shipping implications. International stakeholders are closely watching the impact on trade and relations.
In recent weeks, US President Donald Trump has intensified his rhetoric regarding the Panama Canal, expressing concerns over China’s growing influence and suggesting potential US action to regain control of this strategic waterway.
These statements have reignited debates about sovereignty, international relations and the historical context of US involvement in Panama. At the same time, these tactics are further heightening the already strained relations between the US and China, making the prospect of a full-scale trade war an increasingly likely scenario.
Historical Involvement of US in the Panama Canal
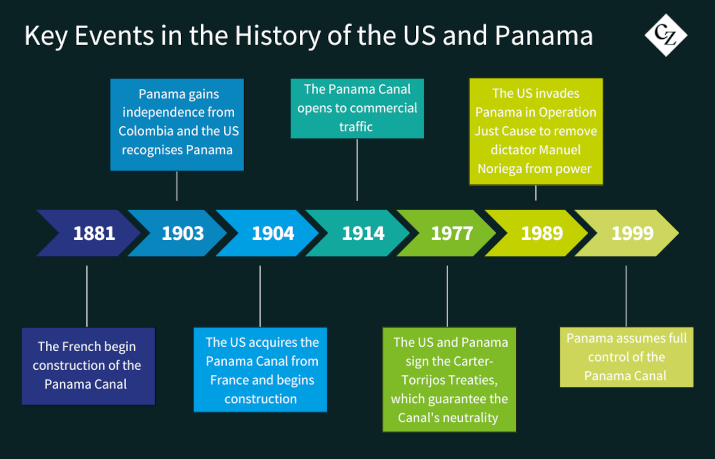
The Panama Canal, completed in 1914, was a monumental engineering feat that significantly shortened shipping routes between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Originally constructed and operated by the US, the canal was transferred to Panamanian control on December 31, 1999, following the Torrijos-Carter Treaties of 1977. This transfer marked the end of decades of US territorial presence in the region.

Ships entering the Miraflores gates in the Panama Canal, Panama, 2016
However, the US has a history of military intervention in Panama, most notably the 1989 invasion to depose dictator Manuel Noriega. This action left lasting scars and has made Panamanians sensitive to any indications of foreign interference. President Trump’s recent comments have resurfaced these memories, causing concern among residents who fear a repeat of past interventions.
Trump’s Panama Canal Criticism Sparks Concerns
President Trump has accused Panama of allowing Chinese entities to exert control over the canal, expressing severe concerns over the increasingly influence of China in the region. He also criticised Panama for imposing high fees on US ships, describing the charges as “exorbitant”.
In a press conference at Mar-a-Lago, when asked to rule out potential military or economic measures against the Panama Canal, Trump responded, “No… I can’t assure you on either of those two,” leaving open the possibility of forceful action.
These statements have been met with strong reactions from both Panama and China. Panama’s president emphasised that the canal “was not a gift” from the US, asserting the nation’s sovereignty over the waterway.
China, in turn, declared that it does not interfere in the canal’s operations, with a foreign ministry spokesperson saying that China does not participate in the management and operation of the canal and has never interfered in the affairs of the canal.
China Expands Role in Panama Canal
China’s involvement in Panama has grown since the two countries established diplomatic relations in 2017. Chinese companies have made significant investments, particularly in port operations. Hutchison Ports, a subsidiary of Hong Kong-based CK Hutchison Holdings, operates ports at both ends of the canal. This presence has raised concerns in Washington about potential strategic advantages for China.
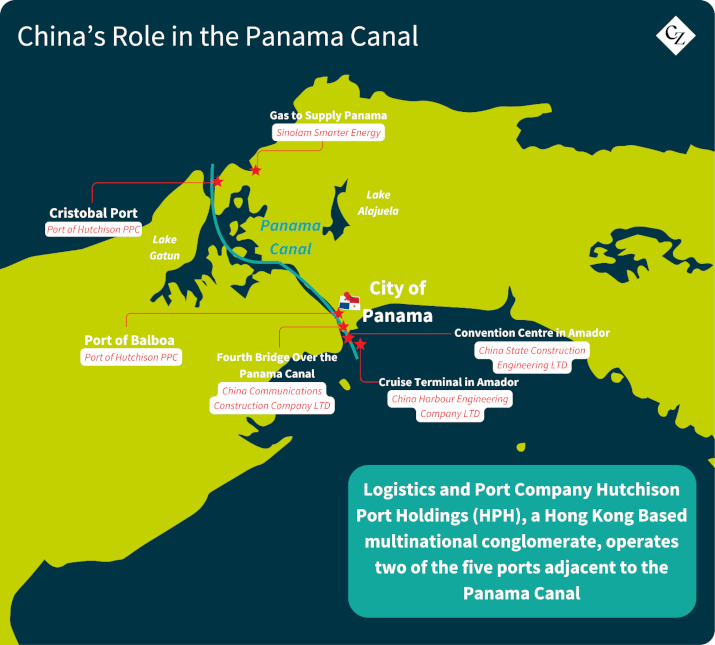
Despite these concerns, Panama maintains that the canal operates under a principle of neutrality, with fees and operations consistent across all nations. Ilya Espino de Marotta, a representative of the Panama Canal Authority, stated that the canal’s operations are impartial and not influenced by any single country. However, Panamanian authorities initiated auditing controls over Hutchison Port’s operations after Trump’s statements.
It is important to note that Hutchison Ports, which operates more than 50 ports globally, is not alone in operating terminal concessions at the entrances to the Panama Canal. Taiwan’s Evergreen Marine Corporation has operated the Colon Container Terminal since 1997, while MSC’s port operating arm TiL signed a concession deal to operate the 2.5 million TEU Panama Colon container port in 2022. Moreover, Seattle-based SSA Marine has operated the Manzanillo International Terminal on the canal’s Atlantic side, since 1995.
Global Powers Weigh in on Panama Canal Debate
President Trump’s remarks have drawn international attention, with various countries expressing their positions.
Russia, for instance, has emphasised the importance of respecting international legal frameworks governing the canal and warned against any form of intervention. The Kremlin stated its commitment to maintaining the canal’s neutrality and cautioned the US against military or economic actions.
These developments highlight the broader geopolitical competition between the US and China in Latin America. The canal, through which approximately 3% of global trade passes, is a critical juncture in this rivalry. Any US initiative to regain control or exert influence over the canal could disrupt global shipping routes and escalate tensions with China.

US Lawmakers Introduce New Legislation
Within the US, there have been legislative moves reflecting the administration’s stance. South Dakota House Representative Dusty Johnson introduced the Panama Canal Repurchase Act on January 9, granting the president authority to negotiate the repurchase of the canal from Panama.
Johnson stated, “America must project strength abroad – owning and operating the Panama Canal might be an important step towards a stronger America and a more secure globe.”
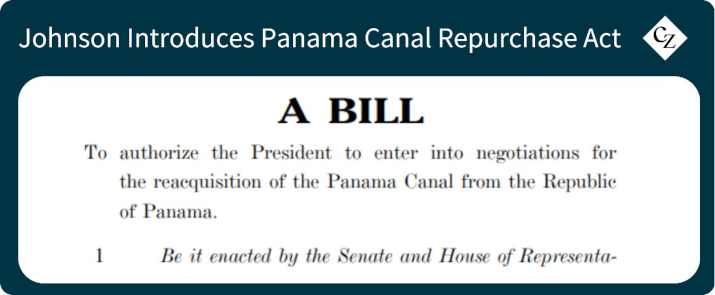
This legislative effort underscores the administration’s concerns about China’s influence over the canal and reflects a broader strategy to counteract Chinese economic and strategic inroads in Latin America.
Trump’s Shift Sparks Uncertainty Ahead
President Trump’s approach marks a departure from previous US policies that emphasised international cooperation and the promotion of democracy.
His focus on reclaiming the Panama Canal aligns with a more assertive, expansionist vision reminiscent of early 20th-century US imperialism. This shift has significant implications for international relations, potentially challenging the current global order and leading to increased tensions with both allies and rivals.
As the situation evolves, it remains to be seen how these dynamics will unfold. The international community, and particularly shipping stakeholders, will closely monitor the actions of the US, Panama, and China. The future of the Panama Canal is not only a regional issue but also a matter of global significance.













