Insight Focus
- The Caribbean used to be a major sugar producing region.
- Today it accounts for less than 1% of global production
- We look at the top sugar producers in the region.
The Caribbean used to be a world hub for sugar production. In the 1740s Jamaica and Haiti were among the world’s foremost sugar producing areas and the Caribbean produced almost all of the sugar consumed in Western Europe. Cuba emerged as a cane powerhouse in the 1800s. Sugar remained a major part of the economy for the region until the early 20th century, but declining access to American and European markets and high costs of production led to an industry-wide decline.
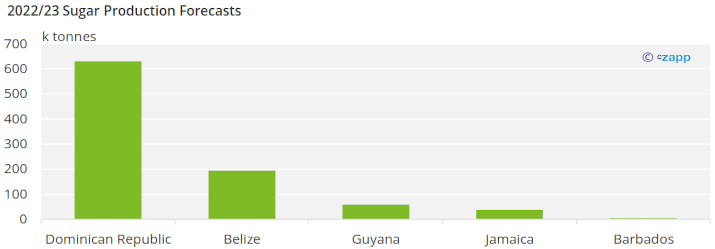
Today there remains significant sugar production in Belize, Cuba and the Dominican Republic, but production in Jamaica, Barbados and Guyana has stagnated. Many Caribbean islands don’t make sugar at all, and the region contributes less than 1% of the world’s sugar production. Let’s look in more detail.
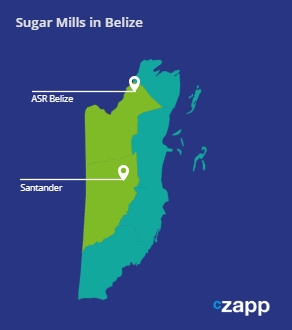
Belize Sugar Production
Belize produces around 190 thousand tonnes of sugar from 2 sugar mills.
Sugar production today is much lower than it was in the 1960s and 1970s thanks to the emergence of smut disease, which leads to stunted cane growth.
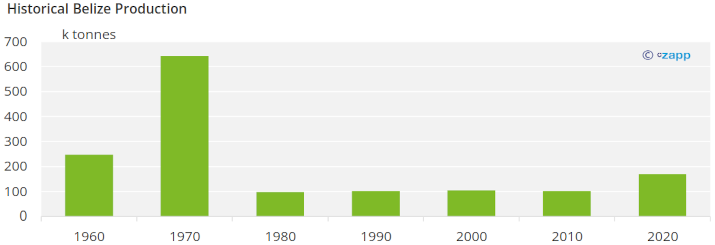
Sugar production in Belize started to increase periodically after the 15/16 season when the second mill in the country, Santander, started production.
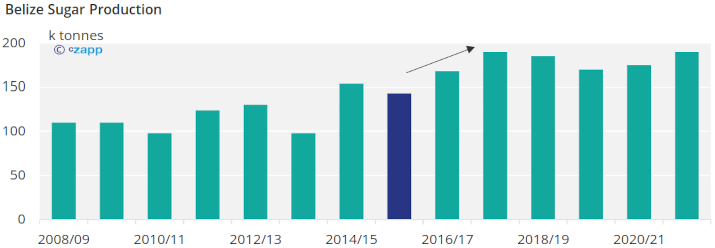
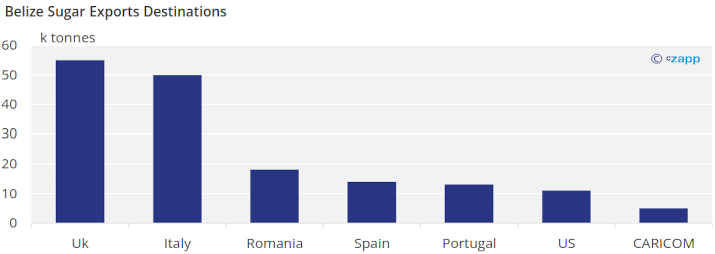
Sugar production in Belize now seems to have stabilised at a little less than 200k tonnes a year. Most of this sugar is exported to Europe, the USA or other Caribbean Community (CARICOM) members.
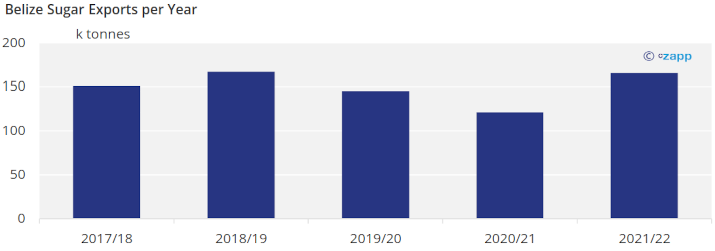
We expect sugar production in Belize to grow, since the second mill in Belize, Santander, is currently expanding their capacity.
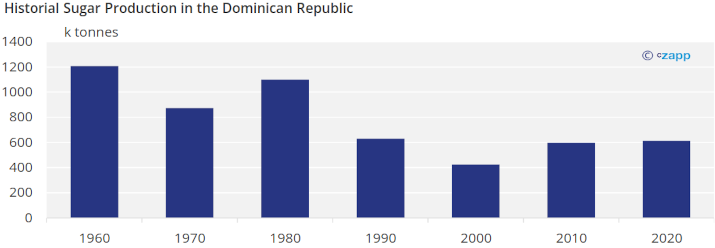
Dominican Republic Sugar Production
Up to the 1980s the Domincan Republic as one of the largest sugar producers in the region. But its reliance on the American market meant that trade suffered as major soft drinks producers switched to high frustose corn syrups in the 1980s, a period which coincided with depressed world market sugar prices. Low returns for sugar led Dominican farmers to switch to other crops.
Today, cane is mostly grown in two zones in the south, in Barahona and Central Romana. The cane is processed by 4 mills to make around 600k tonnes of sugar each year, mostly as raw sugar. Three of the mills are privately held.
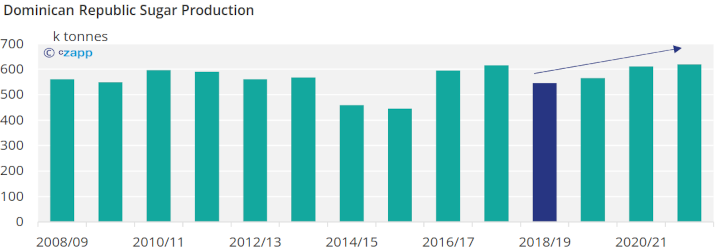
However, the amount of sugar the Dominican Republic produces per year has increased in the past three seasons following the poor crop in 2018/19 caused by bad weather.
The Dominican Republic mainly exports its sugar to the United States. The amount exported depends on how much the United States allocates it in the TRQ quota.
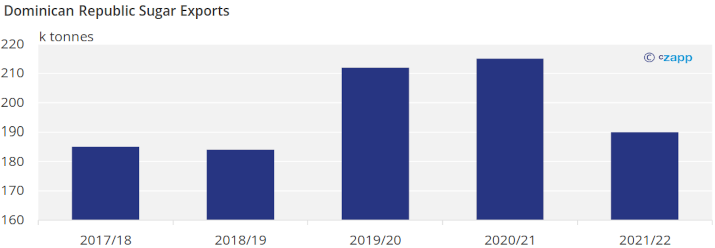
Even though the Dominican Republic produces less sugar than most of its counterparts, it has the largest allocated TRQ quota for the 2023 season.
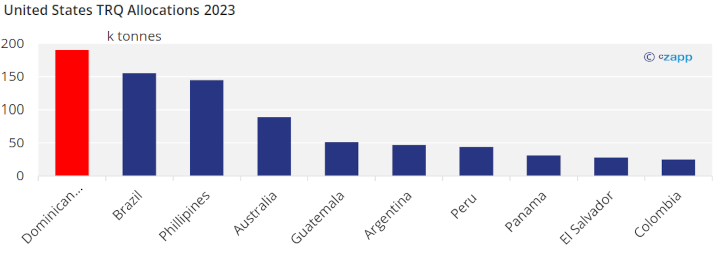
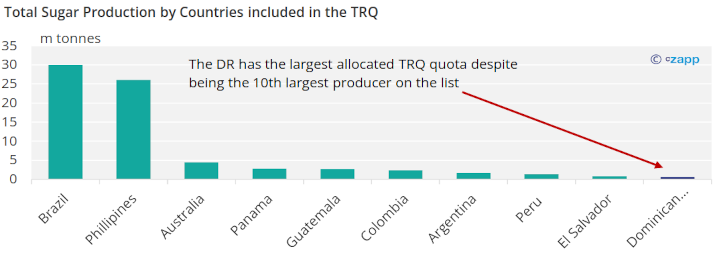
Dominican sugar production should continue to grow since domestic consumption is increasing (reaching pre-pandemic levels) and the Dominican Republic is expected to continue having the largest single-country allocation in the TRQ.
Jamaica Sugar Production
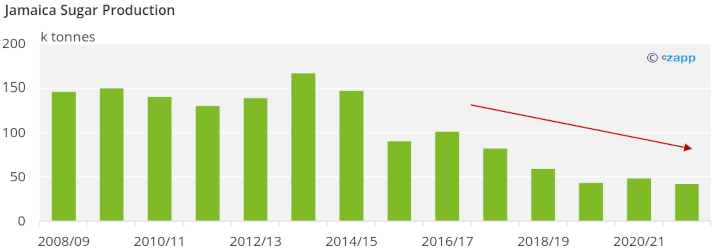
Jamaica was a world leader in sugar production in the 1960s. As with other Caribbean sugar producers, the fall in sugar prices during the 1970s, coupled with the inefficiency of mills and lack of scale, led to a sustained production decrease. Production decreased from 515 thousand tonnes in 1965 to 186 thousand tonnes in 1984 to 48 thousand tonnes in 2022.
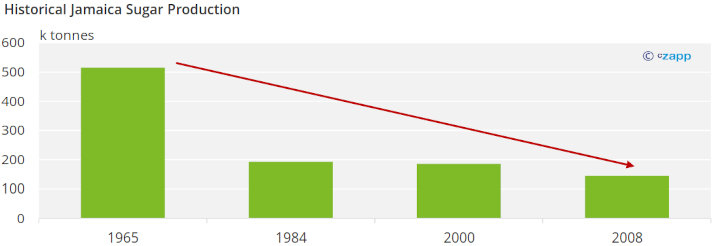
Two mills remain in Jamaica, both making raw sugar. Jamaica produced 42 thousand tonnes of sugar for the 2021/22 season. Production in Jamaica has decreased in five out of the past six seasons. Sugar production in Jamaica fell because of high production costs, lack of labor, and the reallocation of lands. The government took land used for sugar production and allocated it for housing projects and to farm other crops.
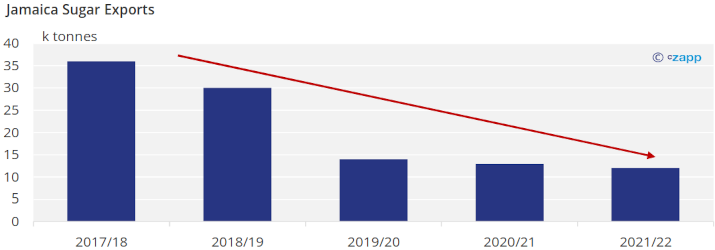
Jamaican sugar exports have also decreased every year for the past five seasons. In 2021, Jamaica could only export half of the 12 thousand tonnes the United States allocated it through the TRQ system.
Sugar production in Jamaica is expected to decrease from 42 thousand tonnes in 2021/22 to 38 thousand tonnes in 2022/23. Sugar production should continue to decline in the following years due to high production costs and lack of labor.
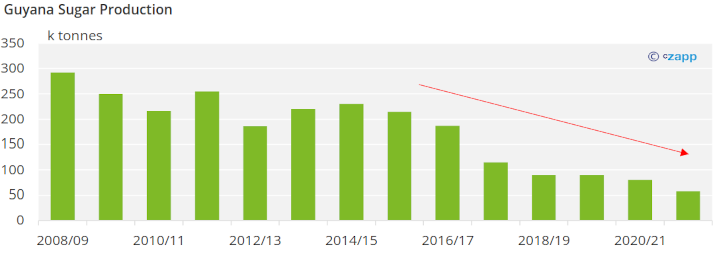
Guyana Sugar Production
In 1971, Guyana produced around 395k tonnes of sugar. In 1976 the government nationalised the sugar industry in the country into the Guyana Sugar Corporation. However, the move was fraught with difficulty. A lack of scale meant that production costs were high, while world sugar prices fell through the 1980s. By 1990 Guyana only produced 130k tonnes and the industry was increasingly dependent on state support and export returns from the EU and USA.
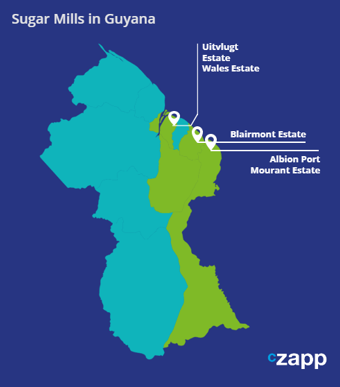
There are currently 3 sugar mills in the Guyana mostly located in the northern part of the country.
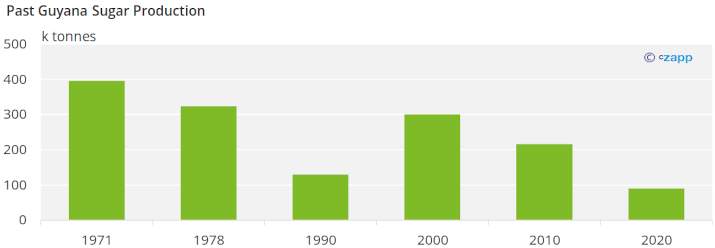
Guyana produced a little less than 58 thousand tonnes of sugar the past season. Its production has also decreased in each of the past seven seasons. Production has decreased in Guyana because of high production costs, unseasonal weather, and labor strikes.
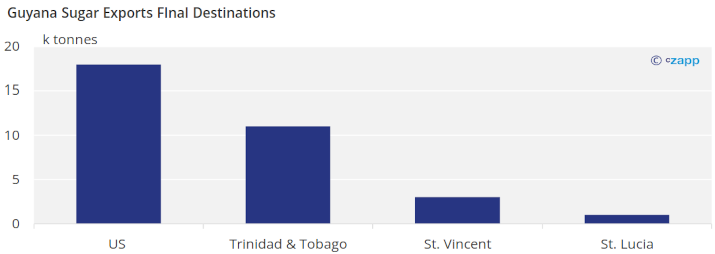
Guyana usually exports its sugar to the United States and to other neighbouring Caribbean nations though CARICOM.
Sugar production in Guyana should continue to decrease in the following years due to the abandonment of plantations because of financial issues and lack of labor.
Barbados Sugar Production
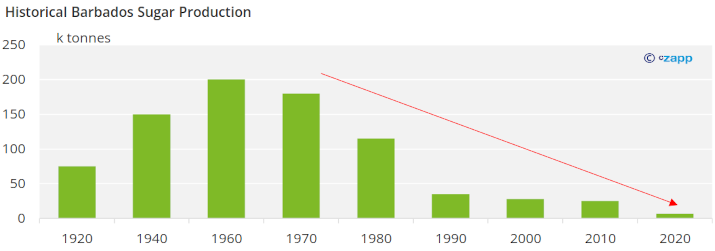
At its peak, Barbados produced around 200 thousand tonnes of sugar in 1960. Falling sugar prices during the 1970s and mills overleveraging caused sugar production between 1960 and 1980 to decrease by 60%. Mills had debts of over 100 USD million during this time. Between 1980 and 1990, production decreased by another 10%.
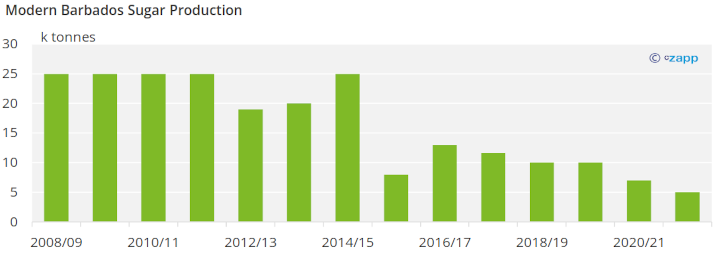
Barbados sugar production has been less than 15 tonnes in the last five seasons. Barbados occasionally exports a few tonnes of sugar to the United Kingdom, but most of the sugar is consumed domestically.
Sugar Trade Within the Region
Belize, Guyana, Jamaica, and Barbados are members of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). CARICOM is a political and economic union that promotes free trade within Caribbean countries. Sugar is traded and is a protected good within CARICOM. Around 20,000 to 40,000 tonnes of sugar is exported from Belize, Guyana, Jamaica, and Barbados to other CARICOM members per year. If raw sugar is imported from a non-member state, the sugar will be liable to a Common External Tariff (CET). If production of white sugar in the region reaches a certain amount then imported refined white sugar is susceptible to the CET.