Insight Focus
Indian sugar prices have been stable in recent weeks. This is despite sugar production being much lower than expected. Raw sugar and refined sugar export margins are negative today.
Maharashtra Sugar Imports/Exports
Domestic sugar prices traded at INR 38,700/tonne at the beginning of the month but have since drifted marginally lower, currently trading at INR 38,500/tonne.
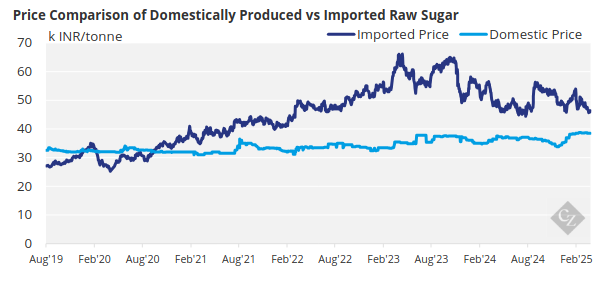
However, given the weakness in the world sugar market and this year’s strength in the Indian Rupee, exports now have a negative margin. Mills earn around 1.6c/lb less by exporting compared to the domestic market.
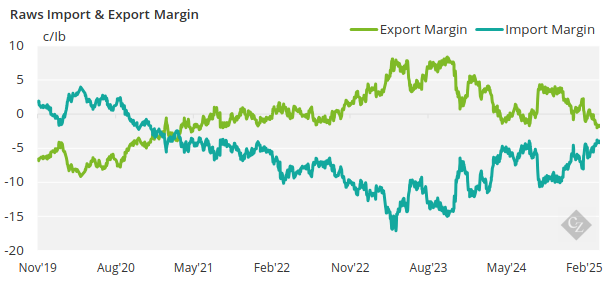
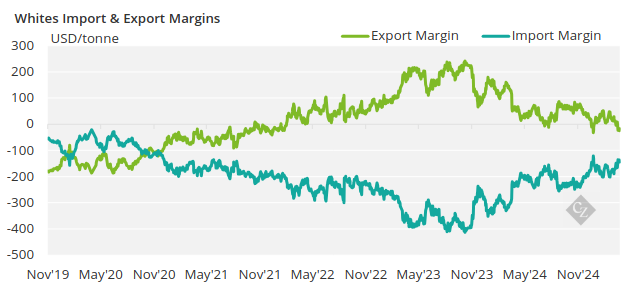
The white sugar export margins are also negative today as mills would earn USD 17/tonne below the domestic market.
Indian sugar production in 2024/25 will be below domestic consumption levels. Most local observers believe stocks are sufficient to meet consumption in 2025. If prices were to keep rising, the government may come under increasing pressure to allow and/or incentivise imports.
Ethanol vs Sugar
Many mills/distilleries have a choice over which feedstocks they use to make sugar or ethanol based on the relative prices of ethanol paid by the oil marketing companies.
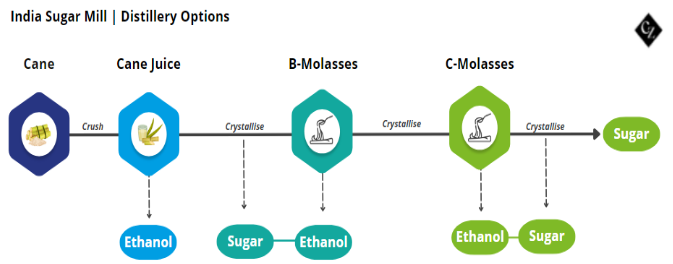
The Indian government has raised prices for C-molasses by 3% for the 2024/25 season to ensure that there is enough ethanol for the Ethanol Blending Program (EBP), as the 20% ethanol blending target is due this year.
Like the current season, the government had incentivised C-molasses production in the previous season to ensure that there was enough sugar supply for domestic consumption as food security was a priority for the government at the time.
The revenue generated by the mills based on the type of feedstock used can be seen in the chart below:
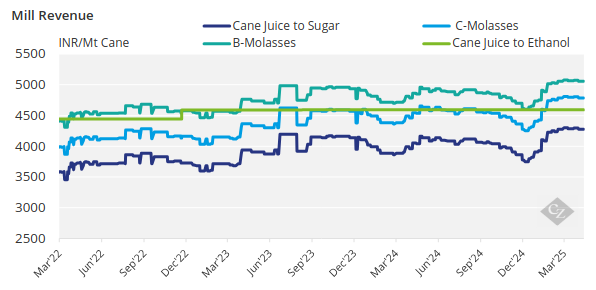
As of last month, India has reached a 20% ethanol blend in petrol 6 years ahead of its original deadline in 2030.
Proportion of Sugar to Ethanol:
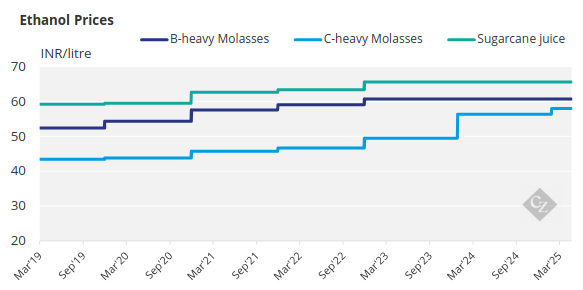
Here are the current prices paid for ethanol by feedstock:
Appendix